|
MOST RECENT ALERTS
There's no recent alert.
|
|
|||||||||||||||
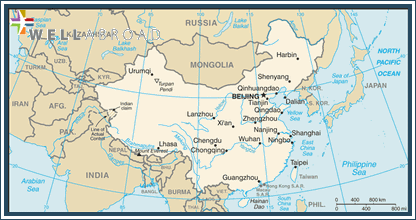
| COUNTRY OVERVIEW | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| COUNTRY GENERAL INFORMATION | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language: |
Standard Chinese or Mandarin (Putonghua, based on the Beijing dialect), Yue (Cantonese), Wu (Shanghaiese), Minbei (Fuzhou), Minnan (Hokkien-Taiwanese), Xiang, Gan, Hakka dialects, minority languages |
||||||
| Currency: | yuan (CNY); note - also referred to as the Renminbi (RMB) | ||||||
| Predominant Religions: |
Daoist (Taoist), Buddhist, Christian 3%-4%, Muslim 1%-2% |
||||||
| National Holidays: | Anniversary of the Founding of the People's Republic of China, 1 October (1949) | ||||||
| Economic Status: |
With well over 1.3 billion citizens, China is the world's most populous country and the third largest country in the world in terms of territory. China is undergoing rapid, profound economic and social change and development. Political power remains centralized in the Chinese Communist Party. |
||||||
| Security: |
People's Liberation Army (PLA): Ground Forces, Navy (includes marines and naval aviation), Air Force (includes airborne forces), and Second Artillery Corps (strategic missile force); People's Armed Police (PAP); Reserve and Militia Forces |
||||||
| US Presence: |
U.S. Embassy in Beijing U.S. Consulate in Chengdu
U.S. Consulate General in Guangzhou
U.S. Consulate in Shanghai
U.S. Consulate in Shenyang
U.S. Consulate General in Wuhan
New World International Trade Tower I No. 568, Jianshe Avenue Hankou, Wuhan 430022 Tel?027-8555-7791
|
||||||
| Document Requirements: |
A valid passport and visa are required to enter and exit China and must be obtained from Chinese Embassies and Consulates before traveling to China. Americans arriving without valid passports and the appropriate Chinese visa are not permitted to enter and will be subject to a fine and immediate deportation at the traveler's expense. Travelers should not rely on Chinese host organizations claiming to be able to arrange a visa upon arrival. Chinese authorities have recently tightened their visa issuance policy, in some cases requiring personal interviews of American citizens. Although a bilateral United States-China agreement provides for issuance of multiple-entry visas with validity of up to one year for tourists and business visitors, Chinese consulates often limit visas to only one entry. Visit the Embassy of China’s website for the most current visa information. Visas are not required of aliens who hold air tickets to the final destination, have booked seats on international airliners flying directly through China, and will stay in a transit city for less than 24 hours without leaving the airport. Persons transiting China on the way to and from Mongolia or North Korea or who plan to re-enter China from the Hong Kong or Macau Special Administrative Regions should be sure to obtain visas allowing more than one entry. Permits are required to visit Tibet as well as many remote areas not normally open to foreigners. A travel permit for Tibet can be obtained through local travel agents. Permits cost approximately renminbi (RMB) 100, are single-entry and valid for at most three months. Most areas in Tibet are not open for foreigners except Lhasa City and part of Shan Nan. Foreigners can be fined up to RMB 500, taken into custody, and deported for visiting restricted areas. For information about entry requirements and restricted areas, travelers may consult the Visa Office of the Embassy of China (PRC) at Room 110, 2201 Wisconsin Avenue, NW, Washington DC 20007, or telephone (202) 338-6688 and fax (202) 588-9760. For a list of services and frequently asked visa questions and answers, travelers can view the Chinese Embassy's web site. There are Chinese consulates general in Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York and San Francisco. The Chinese government has instituted a series of quarantine measures in response to the 2009-H1N1 Influenza. Implementation of the quarantine policies is decided by Chinese officials and sponsoring organizations and may vary by location. Travelers should check frequently with your tour group, sponsoring organization or hotel before traveling to China on what procedures will be in effect for you or your group. Please be advised that host governments, including local authorities, determine the nature and appropriateness of the measures taken in public health matters. In 2007, the Chinese government tightened its regulations for altering or renewing visas for individuals already in China. Visitors can no longer change tourist (L) and exchange (F) -type visas to other types and many applications must now be completed in person. There have also been reports that entry and exit violations are being more strictly enforced, with recent reports of police, school administrators and hotel staff checking to ensure that individuals have not overstayed their visas. Visitors are expected to register with the police within 24 hours of arrival in China. While hotels generally do this automatically with no additional action being required from the guest, Americans planning on staying in private homes with family or friends must go to their local police station to register. The police have been stricter in the enforcement of this rule and have fined apartment companies, hotels and Americans for violations. Americans who overstay or otherwise violate the terms of their Chinese visas will be subject to a maximum fine of 5,000 RMB, departure delays, and may be subject to detention. Travelers should note that international flights departing China are routinely overbooked, making reconfirmation of departure reservations and early airport check-in essential. An airport user fee for both international and domestic flights is now included in the cost of the ticket price. Americans are also required to have an exit visa to leave China. Americans who lose a passport must take into consideration the time needed to get a new passport and a new visa. Visa issuances can take as long as 7 business days. In an effort to prevent international child abduction, many governments have initiated new procedures at entry/exit points. These often include requiring documentary evidence of relationship and permission for the child's travel from the parent(s) or legal guardian if they are not present. Having such documentation on hand, even if not required, may facilitate entry/departure. Dual national Americans, particularly those with dual Chinese and American nationality, should realize that entering China using their non-U.S. passport could mean that the Chinese Government may not afford them the consular protections to which they are entitled. While the U.S. Government will offer consular services to all U.S. citizens regardless of dual nationality, use of other than a U.S. passport to enter China can make it difficult for U.S. Consuls to assist dual national Americans who have been arrested or who have other concerns with the Chinese Government. China does not recognize dual citizenship. U.S. Embassy and Consulate officials are often denied access to arrested or detained Americans who do not enter China using their U.S. passport. Lawful Permanent Residents of the United States who do not carry unexpired Permanent Resident Cards ("Green Cards") or other clear evidence that they may re-enter the United States will encounter delays departing from China. Lawful Permanent Residents should renew and update U.S. residence documentation prior to their departure from the United States. China considers a child born within its borders to hold Chinese citizenship if one parent is a Chinese national, even if the child applies for and receives a U.S. passport while in China. In these cases, when parents want to travel overseas with their child, they should contact their local Public Security Bureau for information on obtaining a travel document (lu xing zhen). |
||||||
| Major Airports: |
Airports: 486, Airports w/paved runways: 403 |
||||||
| Servicing Airlines: |
|
||||||
| Risks and Precautions: |
US Dept of State Travel Alert for CHINA Issued 3 July 2008 |
||||||
| Mortality Statistics: |
Infant MR total: 22.12 deaths/1,000 live births |
||||||
| Immunization Indicators: |
Required: None |
||||||
| Infectious Disease Concerns: |
Malaria risk area in China: Travelers to cities and popular tourist areas, including Yangtze River cruises, are not at risk and do not need to take chemo prophylaxis. Rural areas only of the following provinces: Hainan, Yunnan, Fuijan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, Sichuan, Tibet (in the Zangbo River valley only), Anhui, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, and Shandong. In provinces with risk, transmission exists in rural communities below 1,500 m only during warm weather: north of latitude 33°N, July-November; between latitude 25°N and 33°N, May-December. South of latitude 25°N, transmission occurs year-round. |
||||||
| Overall Quality of Medical Services: |
Western -style medical facilities with international staffs are available in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and a few other large cities. Many other hospitals in major Chinese cities have so-called VIP wards (gaogan bingfang). Generally, in rural areas, only rudimentary medical facilities are available, often with poorly trained medical personnel who have little medical equipment and medications. Rural clinics are often reluctant to accept responsibility for treating foreigners, even in emergency situations. |
||||||
| Providers in Network: |
|
||||||
| Recent Medical Threats/ Concerns/Warnings: |
ALTERNATIVE MEDICAL TREATMENTS: There have been increasing numbers of foreigners coming to China to receive alternative medical treatments or procedures prohibited in the United States relating specifically to stem-cell research. Any person contemplating these treatments should be fully aware of the risks of such procedures. The treatments can be dangerous and untested. The results are not guaranteed. In many instances, patients going for treatment develop secondary infections that cannot be handled by these facilities. They are transferred to hospitals for treatment and are responsible for all additional costs, including repatriation back to the United States. In some cases, these treatments have resulted in death. |
||||||
| Communications Info: |
Country Calling Code: +86 |
||||||






